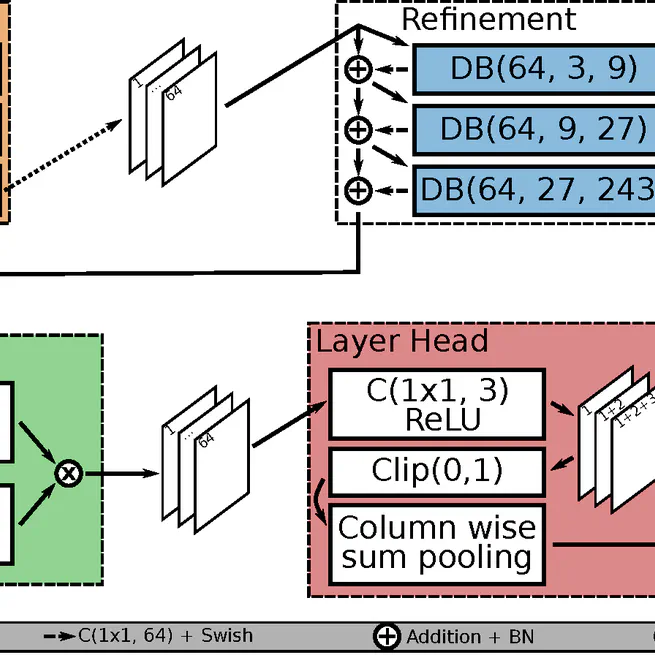
A novel deep learning based architecture that directly predicts the position of layers in OCT and guarantees their correct order is introduced, achieving state-of-the-art results for retinal layer segmentation.
May 19, 2023
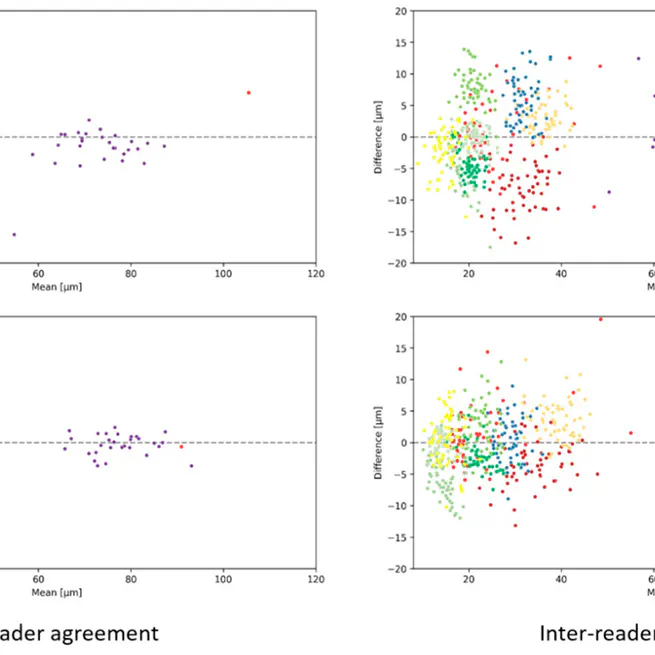
Improved axial resolution of the High-Res OCT benefits retest reliability of retinal layer annotation and improves perceived image quality and resolution and Automated image analysis algorithms could also benefit from the increased image resolution.
Mar 31, 2023
Automated drusen volume measures are not interchangeable between devices and softwares and need to be interpreted with the used imaging devices and software in mind.
Dec 19, 2022
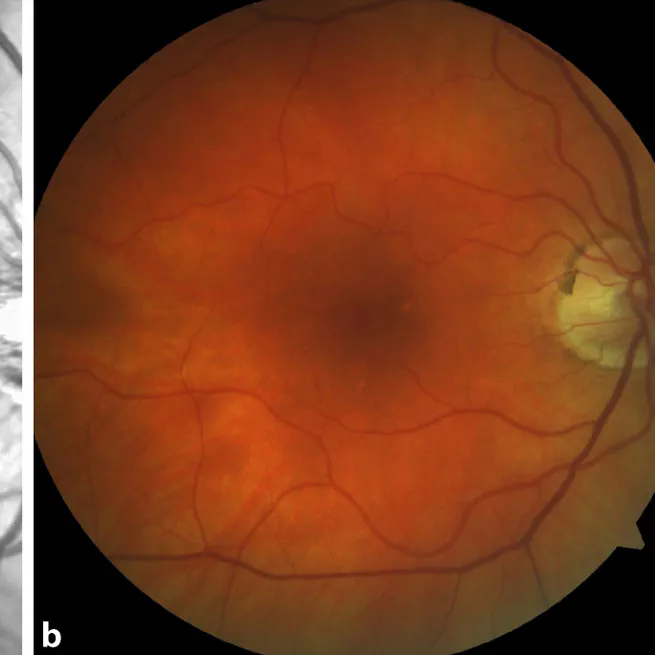
Multimodal imaging has revolutionized retina analysis with detailed imaging and data integration, but the complexity and volume of information require the use of AI, which is becoming increasingly vital for ophthalmologists to understand and utilize in practice.
Aug 26, 2020
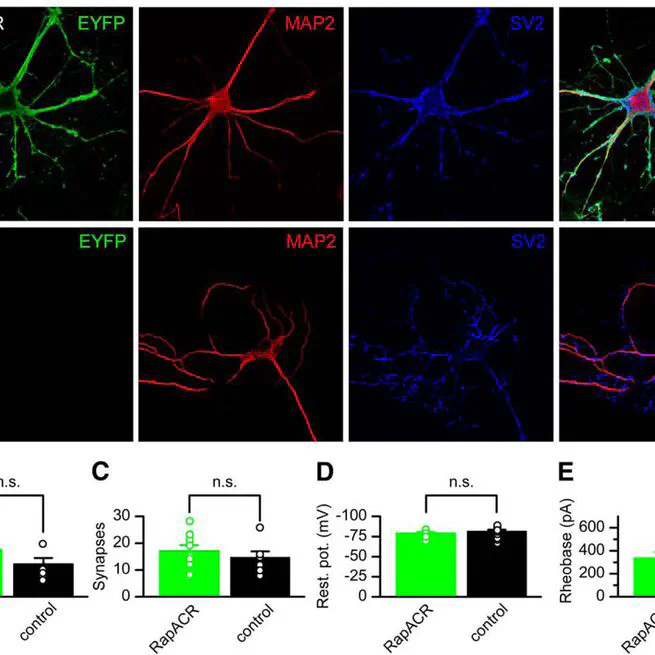
RapACR, nicknamed so for “rapid,” an ACR from Rhodomonas salina, is reported that exhibits channel half-closing times below 10 ms and achieves equivalent inhibition at 50-fold lower light intensity in lentivirally transduced cultured mouse hippocampal neurons as the second-generation engineered Cl–-conducting channelrhodopsin iC++.
May 1, 2018
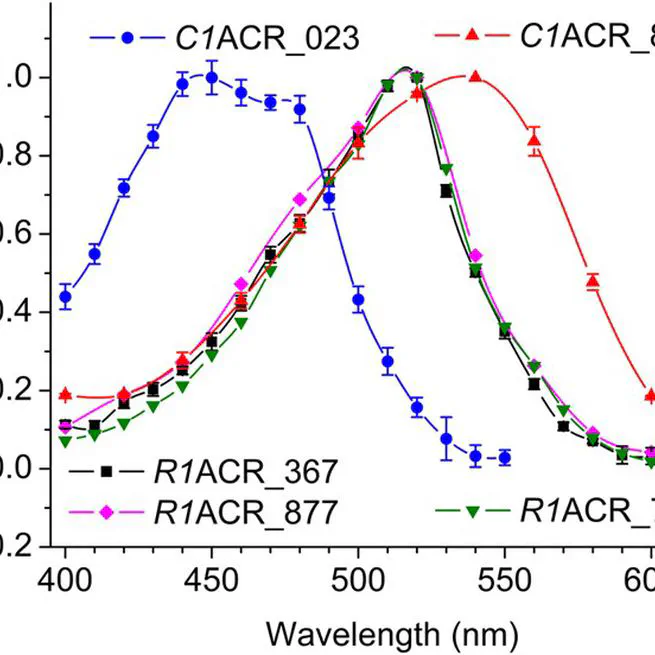
A notable variant, designated “ZipACR”, is particularly promising for inhibitory optogenetics because of its combination of larger current amplitudes than those of previously reported ACRs and an unprecedentedly fast conductance cycle.
Mar 3, 2017